About this Report:
NEW: The heat pump policy toolkit is now available in Korean. You can find that version here.
Heat pumps, a critical technology for clean energy systems, are becoming the most important technology for heating decarbonisation. Currently, the vast majority of heat is provided by fossil fuels. In order to promote and encourage heat pump installations across the globe, the Regulatory Assistance Project, CLASP, the Global Buildings Performance Network, and Agora Energiewende have developed this heat pump policy toolkit—Version 2.0 — which provides a suite of tools, and advice on how to use them, for policymakers interested in promoting this critical technology.
This toolkit works as a synthesis of policy approaches to heat pump deployment and a guide to designing the best packages of policies. The interactive toolkit (which includes clickable links throughout) also features short videos that give an overview of each relevant element of the toolkit.
The is the second version of this toolkit we’ve produced. New material includes:
- Updated and new graphics
- Up-to-date data presented in the text
- The prologue
- Chapter 3 – A section air-blown versus wet systems
- Chapter 4 – A section on large heat pumps
- Chapter 5 – An equity chapter
- Chapter 7 – A section on high quality installers
- Chapter 7 – A section on flexibility
- Chapter 11 – A case studies chapter
Author info
RAP: Richard Lowes (lead author), Duncan Gibb, Jan Rosenow, Louise Sunderland, Samuel Thomas
CLASP: Lina Kelpsaite, Matt Malinowski, Alexia Ross,
Global Buildings Performance Network: Peter Graham, Rehema Kabare, Mugure Njendu
Agora Energiewende: Andreas Graf, Steffen Verheyen
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Heat pumps, a critical technology for clean energy systems, are poised to become the most important technology for heating decarbonisation. Currently, the vast majority of heat is provided by fossil fuels. In order to promote and encourage heat pump installations across the globe, the Regulatory Assistance Project, CLASP and the Global Buildings Performance Network have developed this heat pump policy toolkit, which provides a suite of tools, and advice on how to use them, for policymakers interested in promoting this critical technology.
This toolkit works as a synthesis of policy approaches to heat pump deployment and a guide to designing the best packages of policies. The interactive toolkit (which includes clickable links throughout) also features short videos that give an overview of each relevant element of the toolkit.
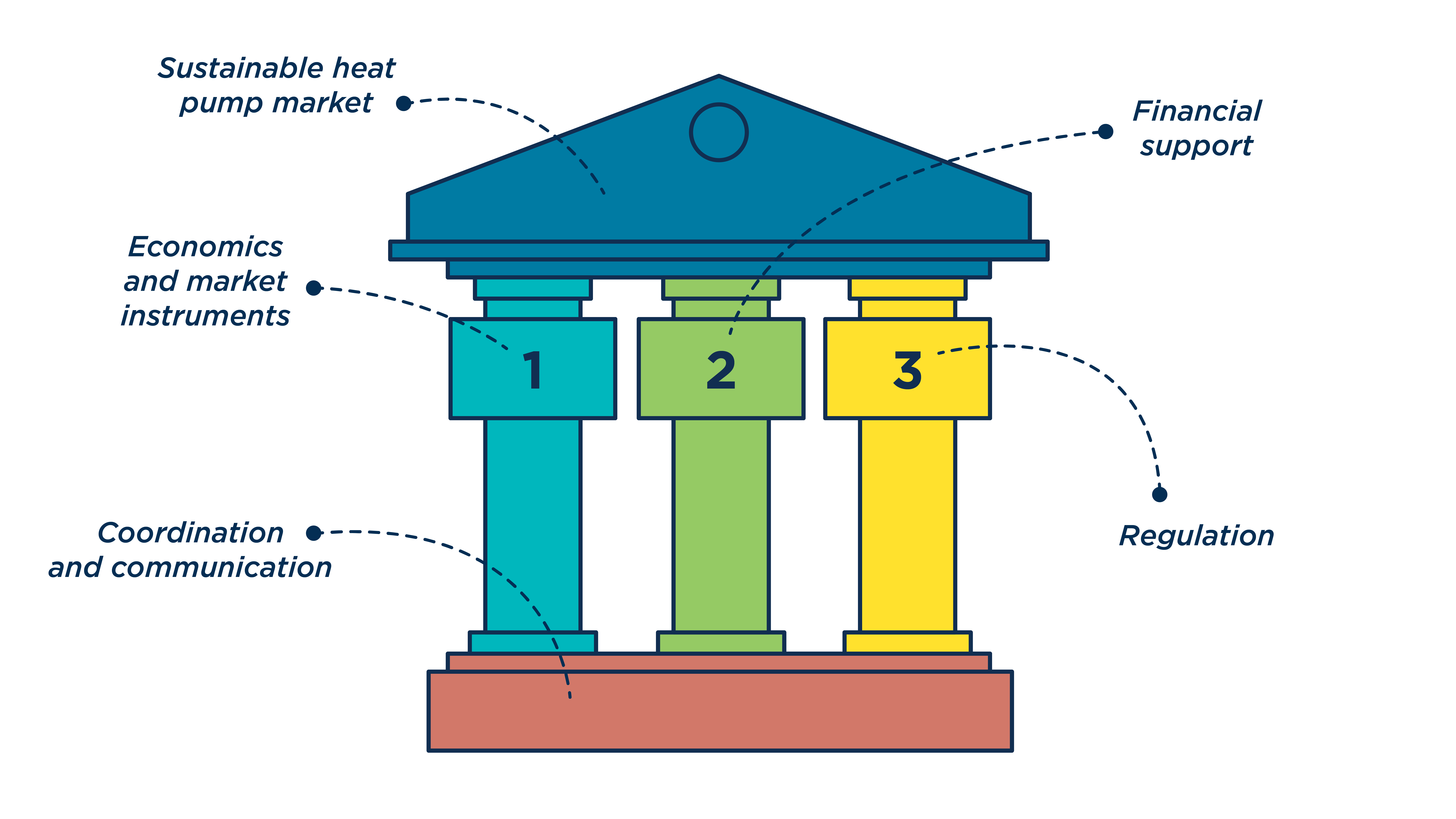
Foundational elements of this toolkit recognise the need for coordination and communication around heat pump policy efforts and strategies.
Pillar 1 considers economic and market-based instruments. These instruments are fundamentally associated with balancing the economics of heat use towards clean options, such as heat pumps, so that their lifetime costs are cheaper than fossil-based alternatives.
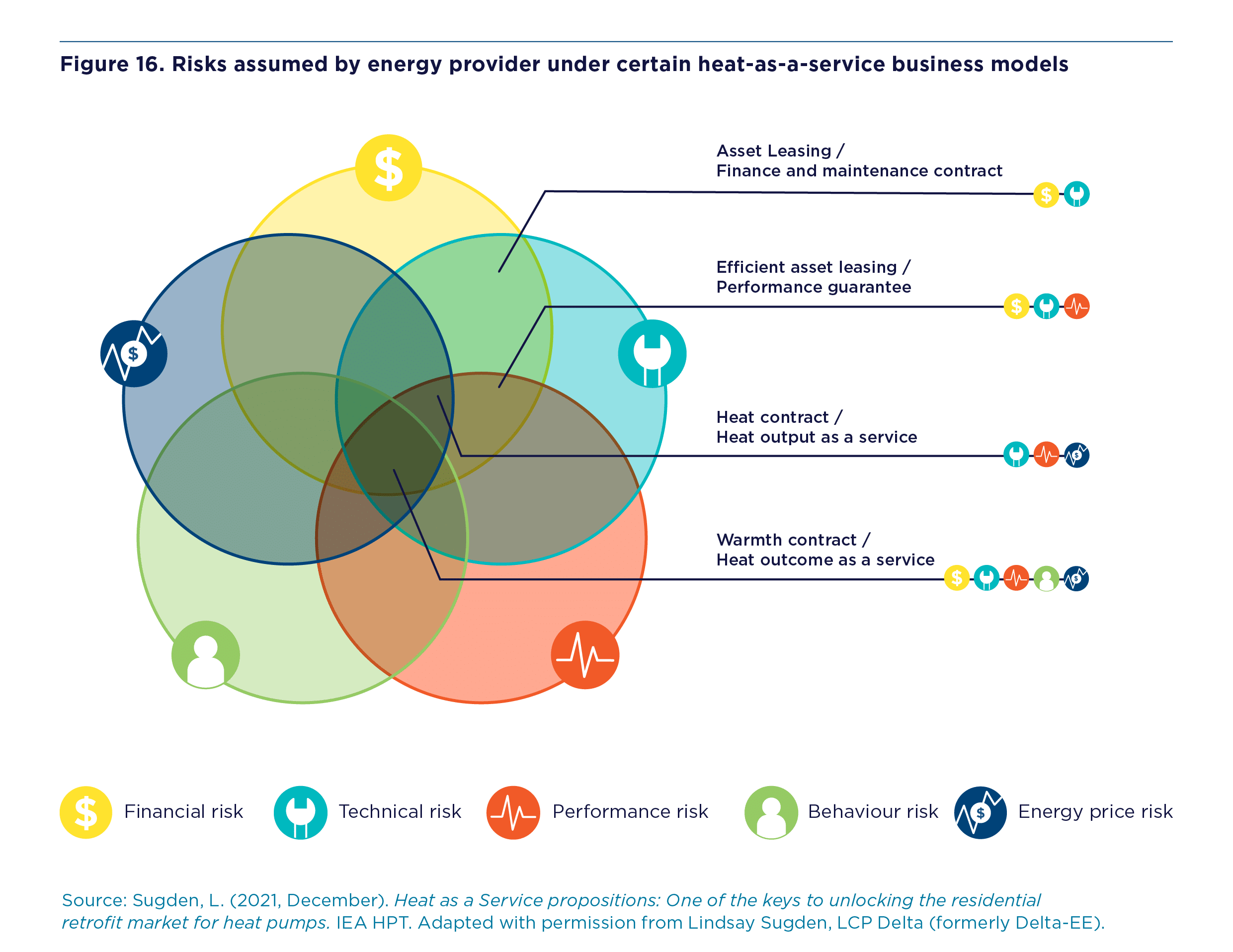
Pillar 2 considers financial support. Within this pillar, we identify three key elements of financial support for heat pumps — grants and tax rebates, loans and heat-as-a-service packages.
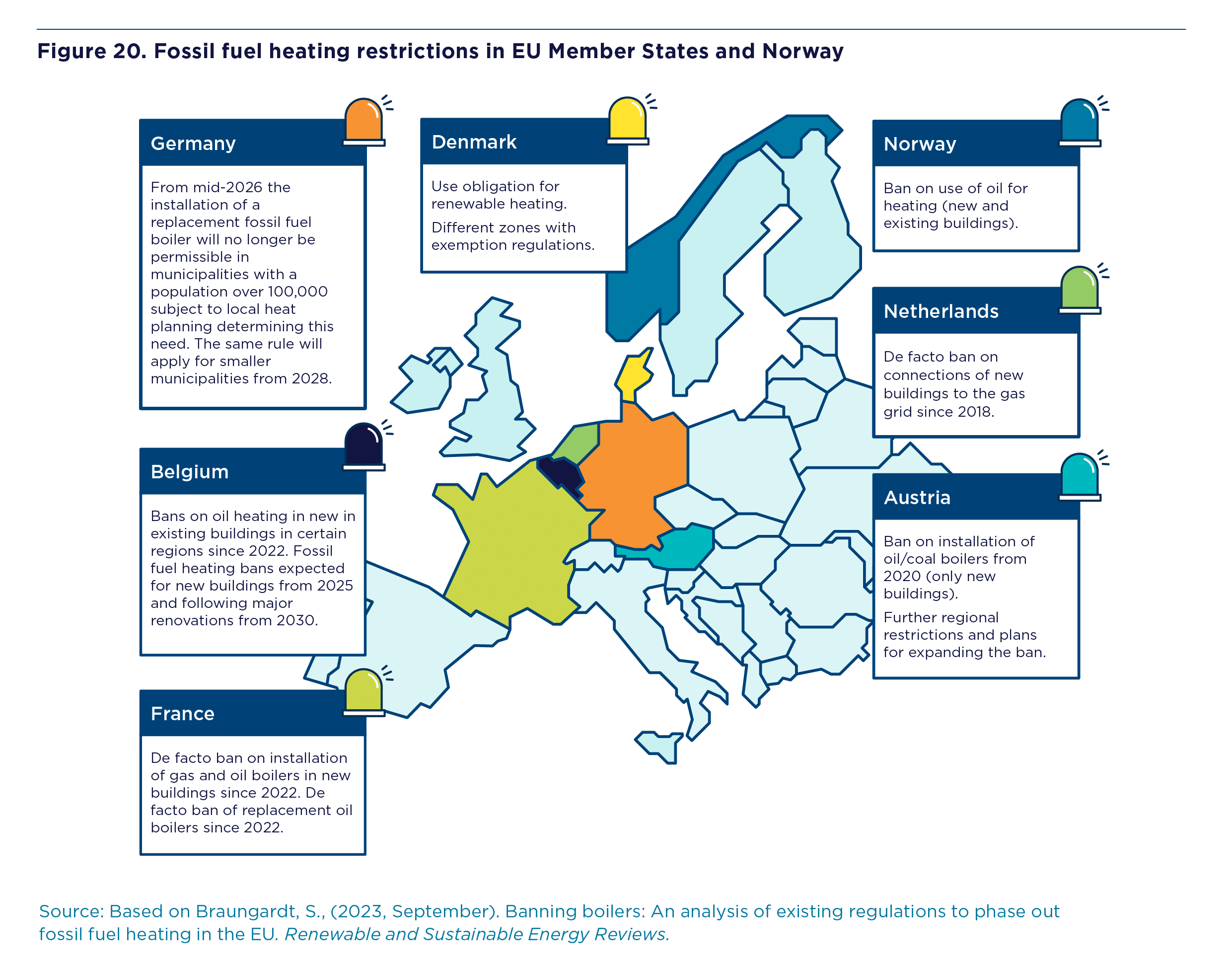
Pillar 3 considers regulations and standards. We look at buildings codes and standards, appliance standards and heat planning and zoning.
To build an effective heat pump policy package, policymakers must consider foundational elements as well as each of the pillars. And even within each pillar, combinations of elements may be appropriate.
HEAT PUMP TOOLKIT VIDEO SERIES:
Check out our video series to learn more about this critical technology for clean energy systems.
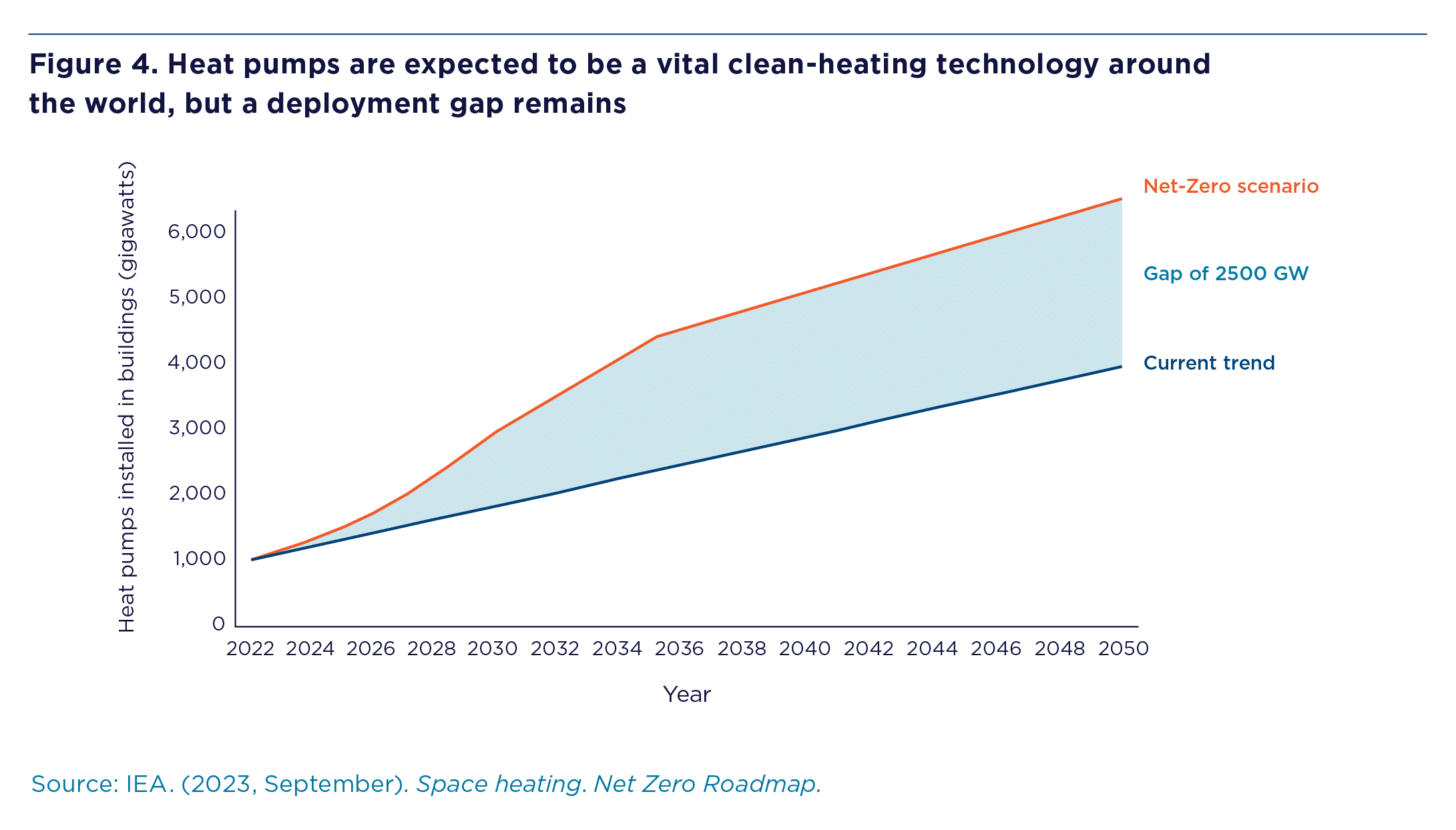
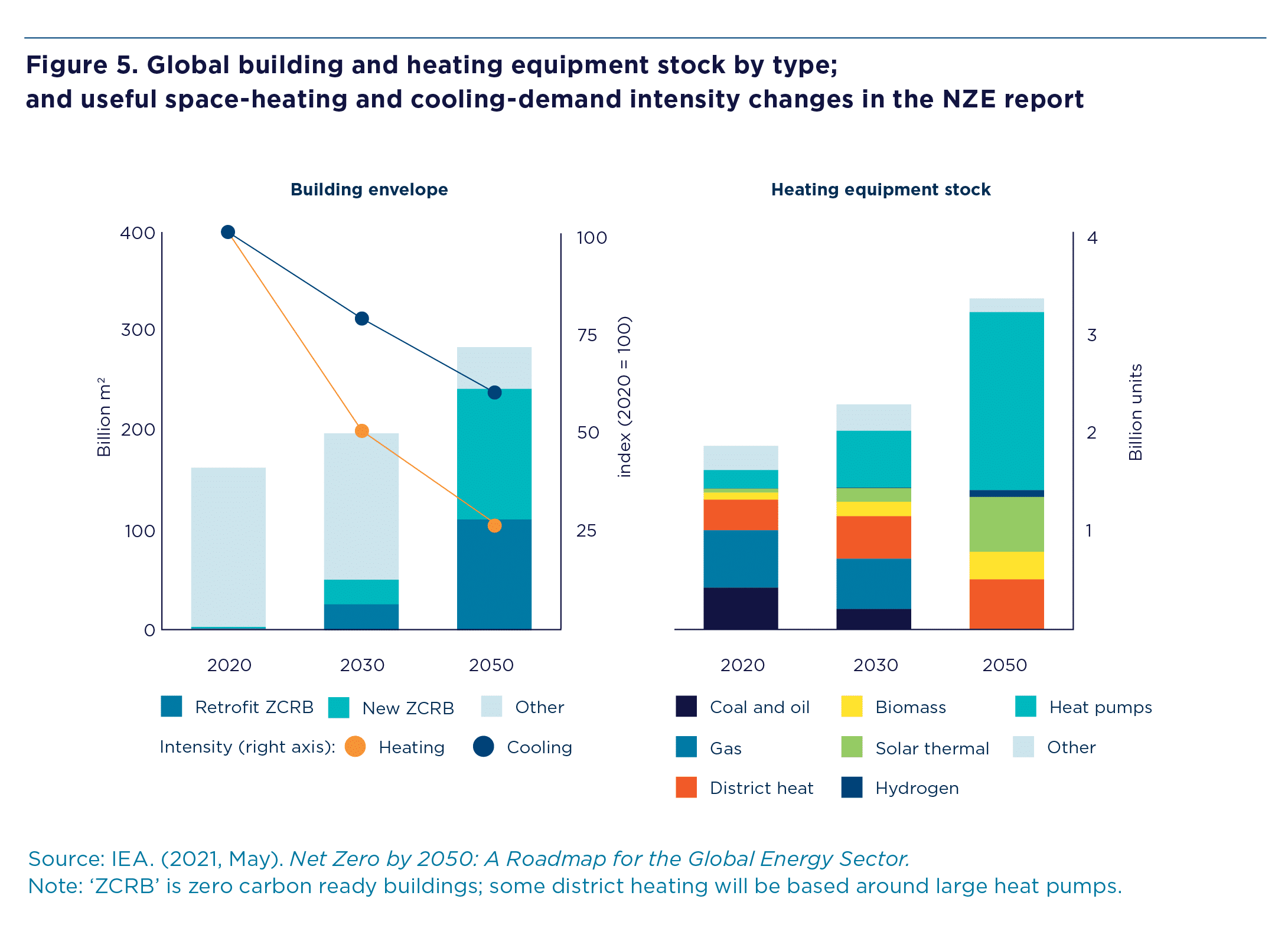
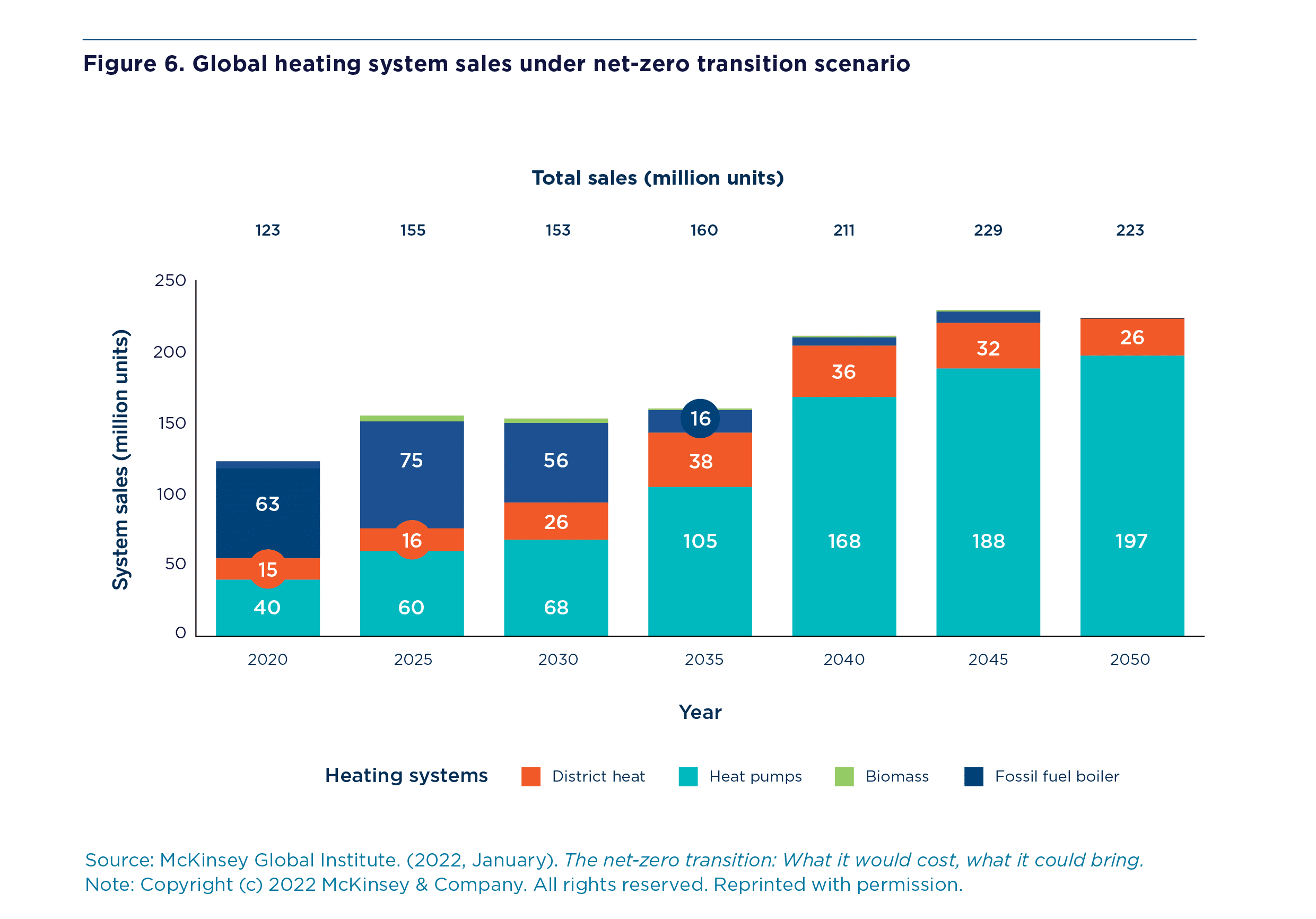
Key Graphics
Download the figures below for more info.